IRQ Tracing
To trace the execution of an interrupt service routine, SystemView provides dedicated APIs to mark ISR entry and exit points.
In the following example, the ISR associated with simple button interrupt is instrumented using SEGGER_SYSVIEW_RecordEnterISR() and SEGGER_SYSVIEW_RecordExitISR() functions:
void sl_button_on_change(const sl_button_t *handle)
{
static uint32_t btn_cnt = 0;
#if defined(SL_CATALOG_SYSTEMVIEW_TRACE_PRESENT)
SEGGER_SYSVIEW_RecordEnterISR();
#endif
if (handle == &sl_button_btn1 &&
sl_button_get_state(handle) == SL_SIMPLE_BUTTON_PRESSED) {
#if defined(SL_CATALOG_SYSTEMVIEW_TRACE_PRESENT)
SEGGER_SYSVIEW_PrintfHost("btn_cnt=%u\r\n", btn_cnt);
#endif
btn_cnt++;
}
#if defined(SL_CATALOG_SYSTEMVIEW_TRACE_PRESENT)
SEGGER_SYSVIEW_RecordExitISR();
#endif
}
The SL_CATALOG_SYSTEMVIEW_TRACE_PRESENT macro is used to conditionally compile SystemView-related code. The SEGGER_SYSVIEW_PrintfHost() function can be used similarly to a standard printf, but less invasive, to transmit information to the host, such as variable values or execution markers.
After compiling and flashing the application, trace capture in SystemView can be started pressing the "Start Record" button. A typical capture result is shown below:
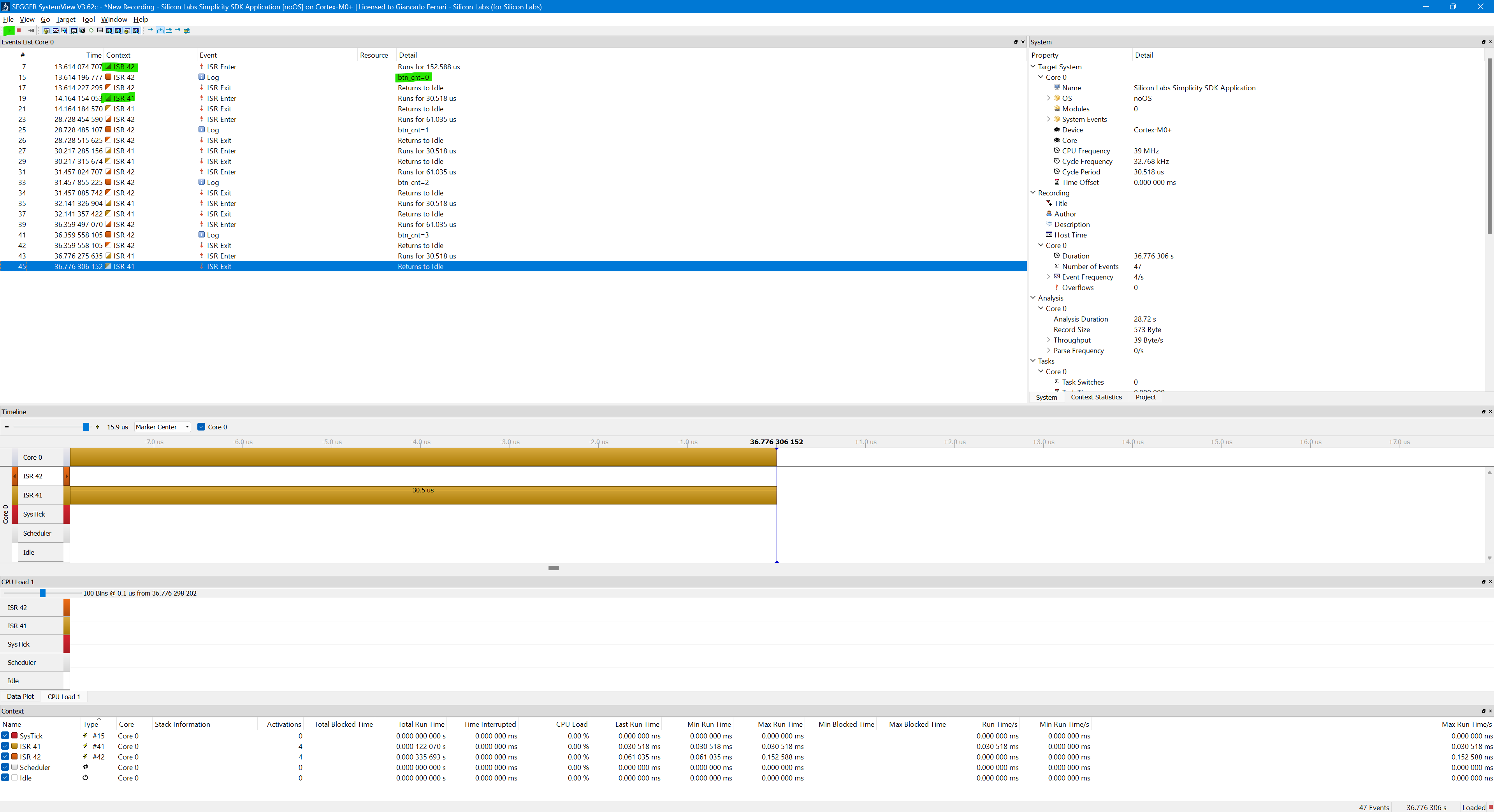
Note: The trace shows that the ISR is invoked twice — once on button press and once on button release. The diagnostic message containing the btn_cnt value is emitted only on the button press event.